Historical Theology and Its Significance
Historical theology is an important field in the study of religion. It helps us understand how people have thought about and practiced their faith throughout history.
In this article, we will explore what historical theology is, why it matters, and how you can study it, including getting a Ph.D. in historical theology. So, let’s dive into the world of historical theology and see why it’s so significant.
What is Historical Theology?

Historical theology is the study of how religious beliefs and practices have developed and evolved over time. It examines the history of theological thought within a particular religious tradition or across multiple traditions. This field of study explores the writings, teachings, and interpretations of religious figures, as well as the cultural and historical contexts that have influenced religious thought. In essence, historical theology helps us understand how and why religious doctrines and practices have changed and adapted throughout history.
What are the Types of Historical Theology Degrees?
There is a lot of knowledge stored in the field of theology. Various competencies and levels are attainable once you start and keep on pursuing theology as a degree or a career path. Here are the types of historical theology degrees:
- Associate in Historical Theology:
- Degree Type: An associate degree is typically a two-year undergraduate program.
- Focus: This degree provides a foundational understanding of historical theology but is generally more general and less specialized compared to higher-level degrees.
- Career Outlook: Graduates may find positions in religious education, ministry support, or continue their education to pursue more advanced degrees.
- Bachelor’s in Historical Theology:
- Degree Type: A bachelor’s degree usually spans four years of undergraduate study.
- Focus: This degree offers a deeper and more comprehensive exploration of historical theology, covering a wider range of topics and historical periods.
- Career Outlook: Graduates can pursue roles in ministry, religious education, pastoral work, or further studies at the master’s or doctoral level.
- Master’s in Historical Theology:
- Degree Type: A master’s degree typically involves one to two years of graduate-level study beyond a bachelor’s degree.
- Focus: This degree delves even further into historical theology, allowing students to specialize in specific eras, theologians, or theological concepts. It often includes advanced research and thesis work.
- Career Outlook: Graduates can teach at the undergraduate level, engage in pastoral leadership, theological writing, or move on to doctoral studies.
- PhD in Historical Theology:
- Degree Type: A doctoral degree is the highest level of academic achievement and can take several years to complete.
- Focus: A PhD in Historical Theology involves extensive research, often resulting in a dissertation that contributes original insights to the field. It provides the highest level of expertise in historical theology.
- Career Outlook: Graduates can pursue careers in academia as professors or researchers, work in seminaries, write scholarly publications, or take on leadership roles in religious organizations.
What are Covered by Historical Theology?

Historical Theology is a fascinating field of study that delves deep into the historical development of Christian beliefs, practices, and traditions. It covers a broad spectrum of subjects, and individuals pursuing a degree in Historical Theology can expect to explore various aspects of Christianity’s history and evolution. Here’s a glimpse of what is covered by Historical Theology:
Subjects Studied:
- Early Christian Thought: This encompasses the study of the writings and theological ideas of early Christian figures like Augustine, Origen, and Athanasius. Students examine the formation of early Christian doctrines and the challenges faced by the early church.
- Church History: Historical Theology involves a comprehensive review of the history of the Christian Church. This includes studying key events, influential figures, and the development of different branches of Christianity, such as Catholicism, Protestantism, and Eastern Orthodoxy.
- Doctrinal Evolution: Students explore how Christian doctrines and beliefs have evolved over centuries. This includes the examination of doctrinal controversies, such as the Arian controversy, and the development of key creeds like the Nicene Creed.
- Theological Movements: Historical Theology covers various theological movements throughout history, such as the Reformation, Scholasticism, and the Enlightenment. Students analyze how these movements influenced Christian thought and practice.
- Hermeneutics: The study of how biblical texts have been interpreted and understood throughout history. This includes the exploration of different methods of biblical interpretation.
- Patristics: This involves the study of the writings and teachings of the early Church Fathers and their contributions to Christian theology.
Requirements:
A degree in Historical Theology typically requires a strong foundation in theology, biblical studies, and church history. Students may need to complete coursework in these areas before specializing in historical theology.
Research skills are crucial, as students often engage in in-depth research on historical theological topics. Many programs also require the completion of a thesis or dissertation on a specific aspect of historical theology.
Future Studies:
Graduates with a degree in Historical Theology can pursue further studies at the doctoral level (PhD in Historical Theology) to specialize in a particular historical period, figure, or theological concept.
They can also explore careers in academia, teaching, research, or writing, contributing to the understanding of Christian history and theology.
Some may choose to work in ministry, using their historical knowledge to inform their pastoral roles and teachings.
In essence, Historical Theology offers a profound exploration of the rich tapestry of Christian thought and history, equipping individuals with a deep understanding of how theology has evolved over time. It opens doors to a range of academic and ministerial opportunities for those passionate about preserving and studying the faith’s historical roots.
Jobs for Historical Theology Graduates
Graduates with a degree in Historical Theology possess a unique skill set that combines historical knowledge, theological understanding, and critical thinking. While the field is specialized, it opens doors to various career opportunities. Here are three common and in-demand jobs for Historical Theology graduates:
- Theology Professor or Educator: Many graduates choose to enter academia and become theology professors or educators. They teach courses in theology, church history, and historical theology at colleges, universities, or seminaries. With the rising demand for theological education, especially in faith-based institutions, there is a consistent need for qualified professors who can impart their knowledge to the next generation of religious leaders.
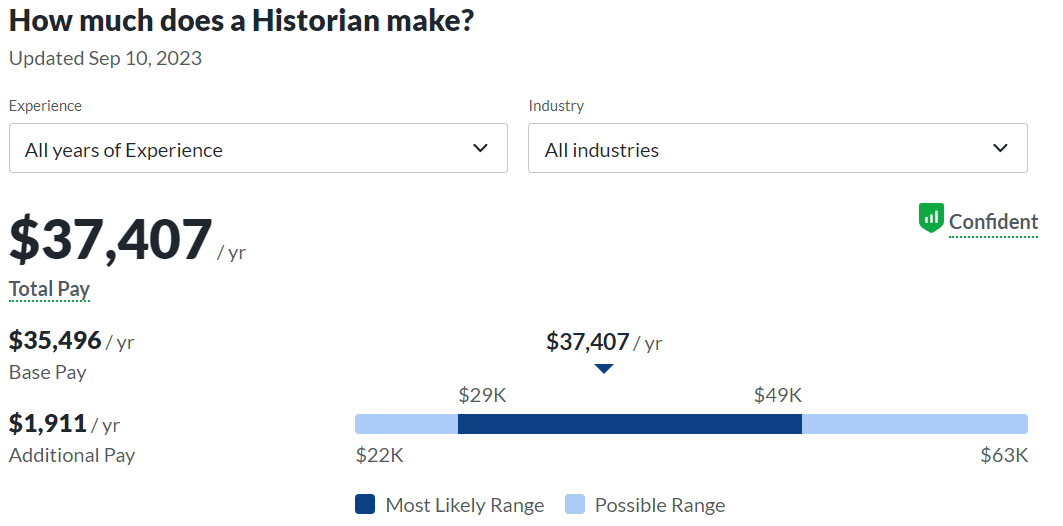
- Religious Writer or Historian: Historical Theology graduates often have strong research and writing skills. They can pursue careers as religious writers, authors, or historians. They write books, articles, and other publications on topics related to religious history, theology, and church development. With the growing interest in religious studies, there is a demand for writers who can communicate complex theological concepts in accessible ways.

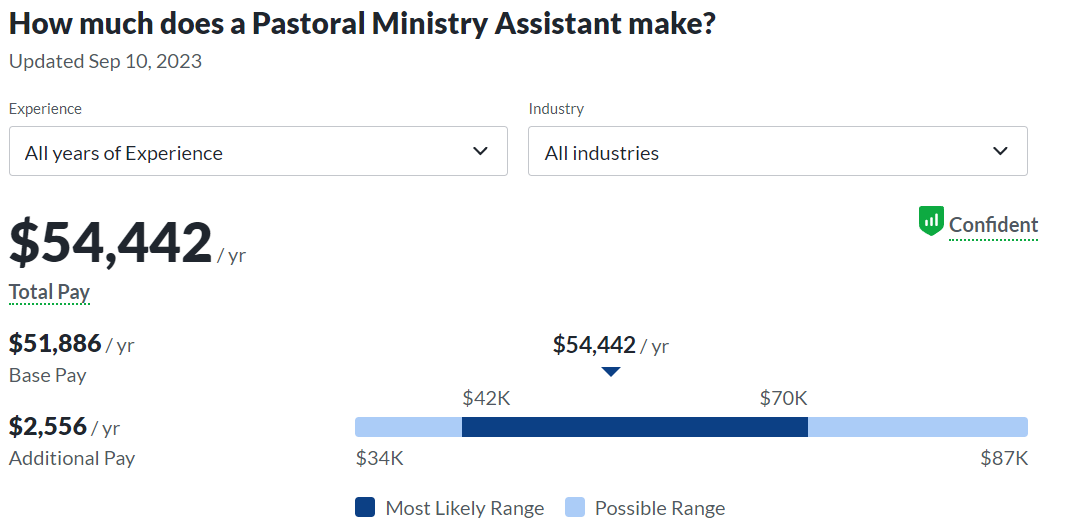
- Ministry and Pastoral Assistance Roles: Some graduates choose to work in ministry and pastoral roles within religious institutions. Their deep understanding of historical theology can inform their preaching and teaching, helping them provide valuable insights to their congregations. They may also take on leadership roles within their religious communities in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of historical theology?
Study of historical theology offers several benefits. It provides insight into the development of religious thought and doctrine over time, fostering a deeper understanding of faith traditions. It equips individuals with critical thinking skills, enabling them to analyze historical texts and theological debates.
Historical theology also helps bridge the gap between tradition and modernity, aiding in the interpretation of religious teachings for contemporary relevance.
What is the significance of philosophy to theology?
Philosophy plays a significant role in theology by providing a framework for exploring fundamental questions about the nature of God, existence, morality, and the human condition. It offers critical tools for rational inquiry and ethical reflection, helping theologians to develop coherent and systematic belief systems.
Philosophy also facilitates dialogue between different faith traditions and with secular worldviews, fostering a deeper understanding of religious doctrines. Overall, it enriches theological discourse, encouraging a more well-reasoned exploration of spiritual and existential questions.
What is the most important aspect of theology?
Theology’s most crucial aspect is its capacity to deepen one’s understanding of the divine and the human relationship with the sacred. It seeks to explore profound questions about the nature of God, the purpose of existence, morality, and the human condition.
The goal is to nurture faith, promote ethical living, and provide spiritual guidance. Ultimately, theology’s significance lies in its ability to inspire individuals to grapple with existential questions, and cultivate a meaningful connection with the divine.
What are the branches of historical theology?
Historical theology encompasses various branches that delve into different aspects of religious history and doctrine. These branches include Patristics, which focuses on the early Church Fathers’ writings and teachings. There’s also Reformation Theology, examining the Protestant Reformation’s theological developments. Additionally, there’s Christology, which explores the nature and identity of Jesus Christ, and Ecclesiology, concerned with the study of the Church. These branches, among others, contribute to a comprehensive understanding of how theology has evolved throughout history.
Is the Bible theological or historical?
One of the oldest books in the world, The Bible is both theological and historical. It contains theological elements, as it presents religious beliefs, doctrines, and moral teachings. Simultaneously, it’s historical because it documents events, people, and cultures from the past, especially in the Old Testament. The Bible intertwines theological messages with historical narratives, making it a complex text that serves both religious and historical purposes.
