Types of Political Science
Political Science, the study of government, politics, and policy, leads to a diverse tapestry of disciplinary branches. In this article, we’ll explore key facets within the different types of political science degrees, diving into political systems and theory. From Comparative Politics to International Relations, every single branch to be mentioned offers unique insights.
Comparative Politics

In the different types of political science degrees, Comparative Politics emerges as a pragmatic approach to understanding the complexity of global politics. This exploration delves into the fundamental aspects of Comparative Politics, shedding light on the significance of comparing political systems, the vast research methodologies applied in the real world, and the practical career possibilities from this field.
Comparing Political Structures Across Borders
Comparative Politics serves as the compass guiding us through an examination of the diverse political structures that govern nations worldwide. From parliamentary systems to electoral processes, this field analyzes the organizational frameworks that shape governance. Through analysis of the similarities and variations among political institutions throughout the globe, researchers gain profound insights in the global political structures across borders..
In essence, this comparative approach provides a holistic understanding of how different countries navigate the complex terrain of political organization, offering valuable lessons and potential avenues for improvement.
Research Methods: From In-Depth Exploration to Statistical Patterns
At the core of Comparative Politics, one of the major types of political science, lies a diverse array of research methodologies, ranging from in-depth case studies to complex statistical analyses. The discipline employs a comprehensive toolbox, allowing competent researchers to delve deep into specific political scenarios while also revealing the most common trends and practices in the global political dynamics.
Case studies offer a qualitative lens, enabling scholars to understand the contextual intricacies of the political field. This in-depth exploration provides a rich foundation for valuable insights and, basically as it is, tested ideas, offering a closer look at the unique factors influencing political systems.
On the flip side, statistical analyses provide a quantitative perspective, allowing researchers to identify trends and correlations across a broader spectrum. This method facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of political dynamics, through numerical figures and statistical trends.
By combining these qualitative and quantitative approaches, Comparative Politics, ideally, ensures a well-rounded, unbiased, and comprehensive understanding of political processes.
Most Common Careers in Comparative Politics
In the dynamic realm of Comparative Politics, multiple career opportunities that have a global impact are present. Here, we present the top careers, each contributing uniquely to the study of political landscapes.
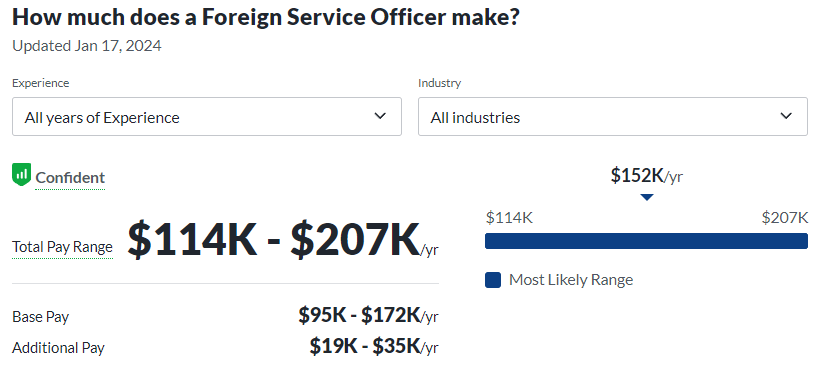
- Foreign Service Officer: Representing a country on the international stage, these professionals engage in diplomatic relations and contribute to policy formulation, fostering positive global interactions.
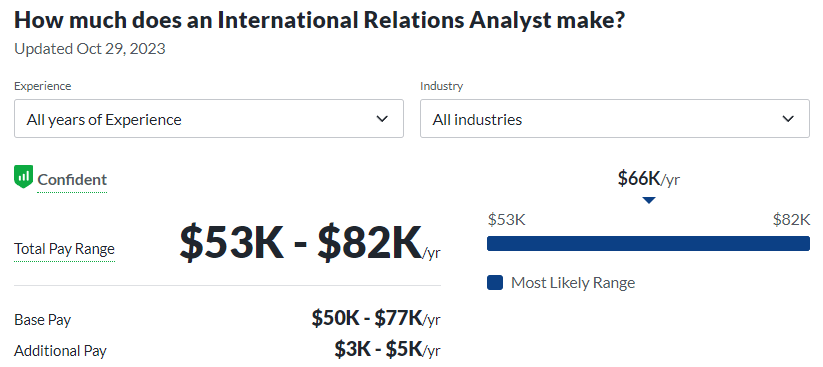
- International Affairs Analyst: Playing a pivotal role in government agencies or think tanks, these analysts analyze global political trends. Their strategic recommendations contribute to informed decision-making, shaping effective international policies.
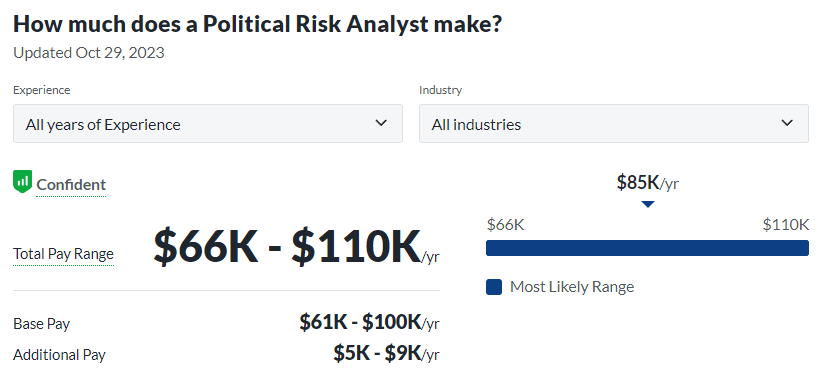
- Political Risk Analyst: Assessing potential political risks for businesses and government agencies, these analysts offer insightful recommendations for international ventures. Expertise in this position includes risk-informed decision-making and critical thinking all for the purpose of maintaining and improving global stability.
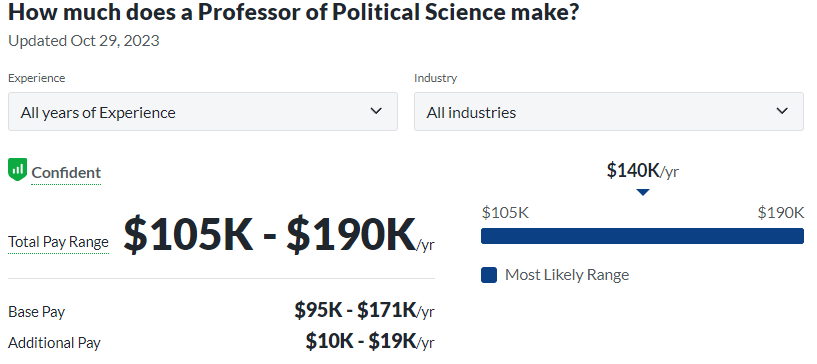
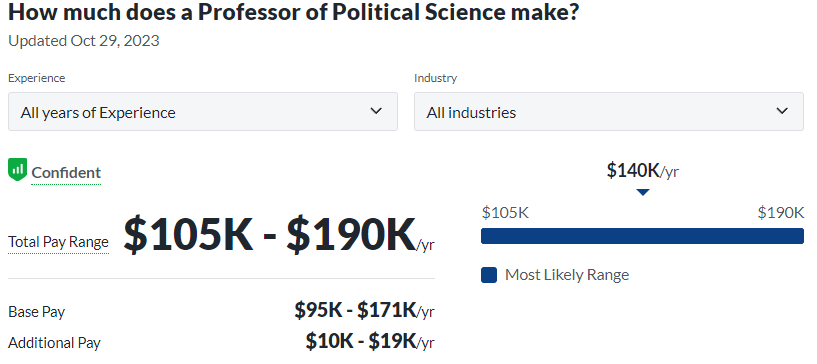
- Political Science Professor: Educating the next generation of political scientists, these professors not only impart knowledge but also conduct research, publish work, and contribute to the advancement of the field. They play a vital role in shaping the future political scientists.
By comparing institutions, scrutinizing processes, and employing diverse research methods, this discipline equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complex global arena. Furthermore, promising career opportunities exist in the field of Comparative Politics, making it an invaluable and dynamic field that benefits not only the political scientists themselves but the global stakeholders as well.
International Relations
Among the different types of political science, International Relations dives into the intricate dynamics that shape global interactions, examining how countries strategically engage, address conflicts, and collaborate on the international stage. From the nuanced study of foreign policy to the critical analyses of national security and the global economy, this discourse aims to unravel the multifaceted layers that define the interconnected world we inhabit.
How Countries Interact on the Global Stage
The examination of how countries interact involves delving into the nuanced dynamics of diplomatic negotiations, international agreements, and the complexities of conflicts and collaborations. Scholars in this discipline aim to uncover the underlying factors that influence the relationships between nations, offering insights into the evolving geopolitical landscape.
Areas like Foreign Policy, National Security, Global Economy
The study of International Relations delves into pivotal areas crucial for understanding the intricacies of the global landscape. Analyzing foreign policy unveils how nations strategically engage, forming alliances, and addressing conflicts diplomatically. Within the realm of national security, scholars and practitioners scrutinize the measures countries employ to safeguard their interests, exploring military strategies, intelligence initiatives, and diplomatic solutions. Additionally, the examination of the global economy provides crucial insights into international trade, financial cooperation, and economic policies, influencing the prosperity and stability of nations on a global scale.
Careers in this Specific Field
Emerging from an International Relations background, careers play pivotal roles in shaping global harmony and societal well-being.
- Diplomats: Serving as crucial conduits for international dialogue, diplomats foster peaceful resolutions and positive diplomatic relations, contributing to global cooperation.
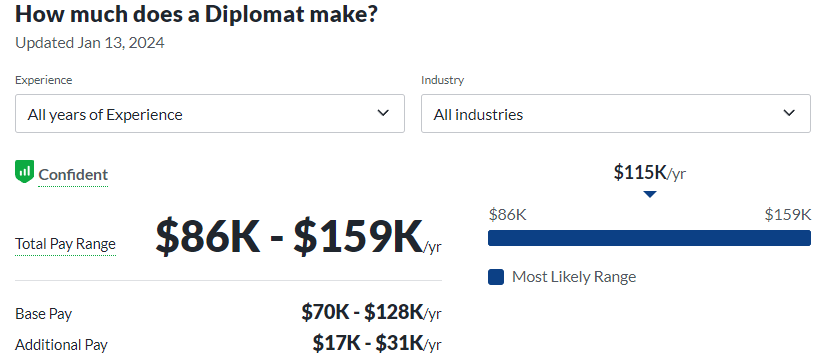
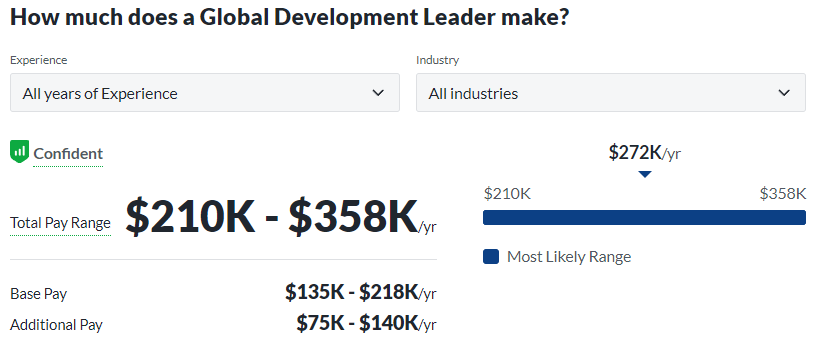
- Global Development Professionals: Actively contributing to sustainable solutions, these individuals address global challenges such as poverty, healthcare, and education on an international scale, promoting societal well-being.
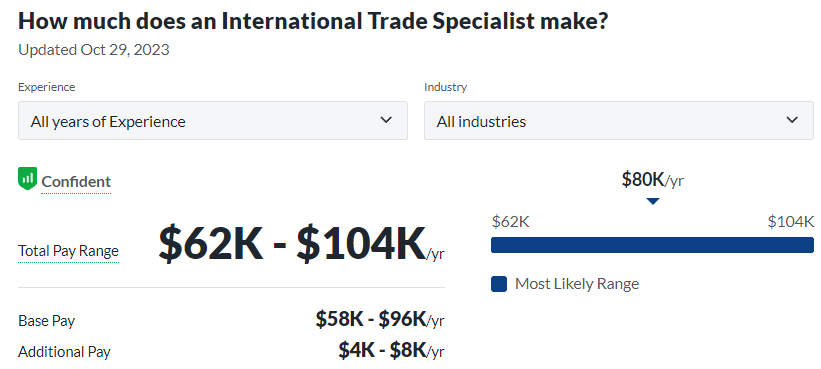
- International Trade Specialists: Facilitating economic cooperation, trade specialists foster growth and stability on a global scale, contributing to economic prosperity and diplomatic ties.
- NGO Workers: Individuals in non-governmental organizations actively contribute to addressing social issues, providing humanitarian aid, and advocating for human rights, embodying the values of compassion and global citizenship. Collectively, these careers exemplify the importance of International Relations in creating a more interconnected and harmonious global community.

Public Administration
In this exploration of Public Administration, we embark on an insightful journey into the intricate dynamics that govern governmental functions and operations. From the fundamental study of how governments operate to the critical examination of issues like budgets, personnel management, performance evaluations, and regulatory frameworks, this part of the article seeks to discuss the multifaceted layers of public governance.
Coverage
Public Administration, one of the main types of political science, serves as the linchpin for comprehending the functions and operations of governments at various levels. It involves the study and implementation of policies, programs, and strategies that contribute to the effective functioning of public institutions. This encompasses a comprehensive examination of how governmental bodies plan, organize, and execute public policies for the welfare of societies.
Issues like Budgets, Personnel, Performance, Regulations
Delving into the core of Public Administration reveals a nuanced exploration of critical issues, including budgetary considerations, personnel management, performance evaluations, and regulatory frameworks. Budgets are meticulously analyzed to allocate resources efficiently, personnel management strategies are devised to ensure a skilled and motivated workforce, performance metrics are scrutinized for optimal efficiency, and regulations are crafted to govern public actions in accordance with societal needs.
Top Careers in Public Administration
- Public Administrator: Public administrators play a pivotal role in overseeing the day-to-day operations of government agencies. They formulate policies, manage resources, and ensure the efficient delivery of public services, contributing to the overall well-being and functionality of communities.
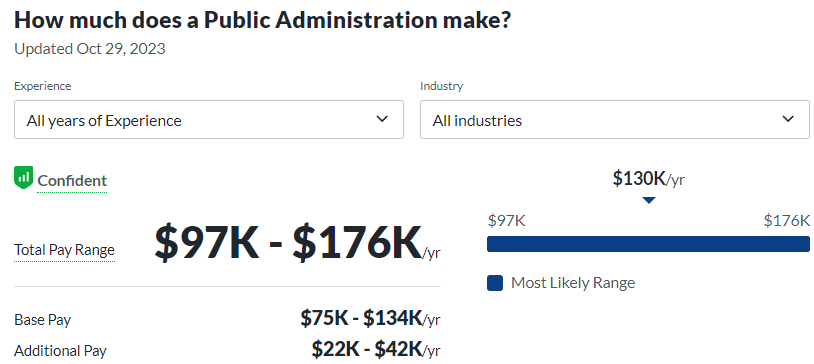
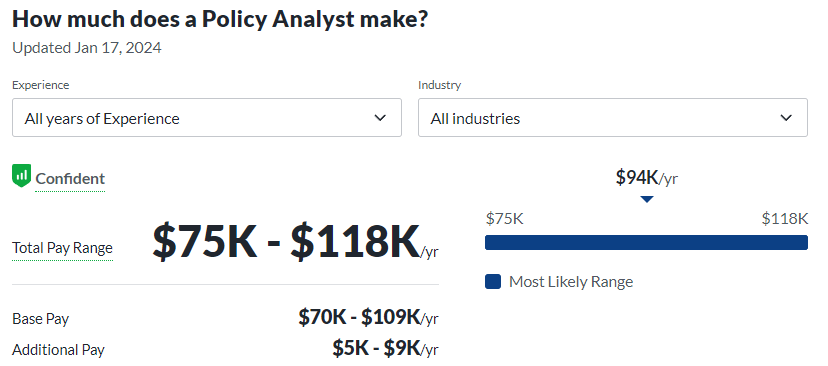
- Policy Analyst: Policy analysts are critical thinkers who assess existing policies and propose improvements. By conducting thorough analyses of social, economic, and political issues, they contribute to the development of effective and impactful policies that address societal needs.
- Urban Planner: Urban planners contribute to the development of cities and regions by designing land-use plans and policies. They strive to create sustainable, efficient, and livable communities, addressing societal needs for housing, transportation, and environmental conservation.

These careers collectively define the essence of Public Administration, as each professional contributes uniquely to the effective functioning and progress of public institutions, fostering a society that is well-managed, responsive, and geared towards the betterment of its citizens.
Political Theory
In this exploration of Political Theory, we delve into the intellectual landscape that studies the political ideas and ideologies shaping the foundations of various political systems. From the intricate examination of familiar concepts like democracy, capitalism, human rights, and social justice, this part of the discussion seeks to unravel the influence that political theories which have existed for decades exert on societal structures and governance.
Studies Political Ideas and Ideologies that Shape Systems
Political Theory serves as the intellectual compass for understanding and dissecting the political ideas and ideologies that underpin diverse systems. Scholars in this field scrutinize the philosophical foundations of political thought, exploring the evolution of ideas that have shaped societies throughout history and continue to influence contemporary political landscapes.
Areas like Democracy, Capitalism, Human Rights, Social Justice:
The study of Political Theory encompasses crucial areas, each with distinctive ideological underpinnings.
- Democracy:
Democracy, a foundational political idea, revolves around the principles of representation and the participation of citizens in decision-making processes of the political structure. Political theorists examine how democratic ideals shape governance structures, policies, and the relationship between the state and its citizens.
- Capitalism:
Capitalism is an economic and political system emphasizing private ownership, free markets, and individual enterprise. Political theorists analyze the impact of capitalist ideologies on economic systems, wealth distribution, and the role of government in regulating the hence competitive markets due to this specific political ideology..
- Human Rights and Social Justice:
Human rights and social justice represent moral and ethical dimensions of political theory. Scholars explore the theoretical foundations of human rights, aiming to understand the principles that safeguard individual freedoms and promote equality.
Top 5 Careers/ Career Paths:
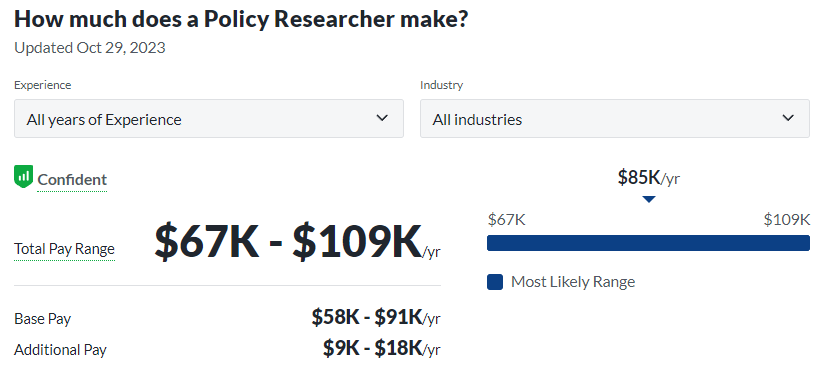
- Law: Political theorists specializing in law contribute to legal scholarship by interpreting and shaping laws based on a deep understanding of political ideologies. They play a vital role in ensuring that legal frameworks align with principles of justice and governance.
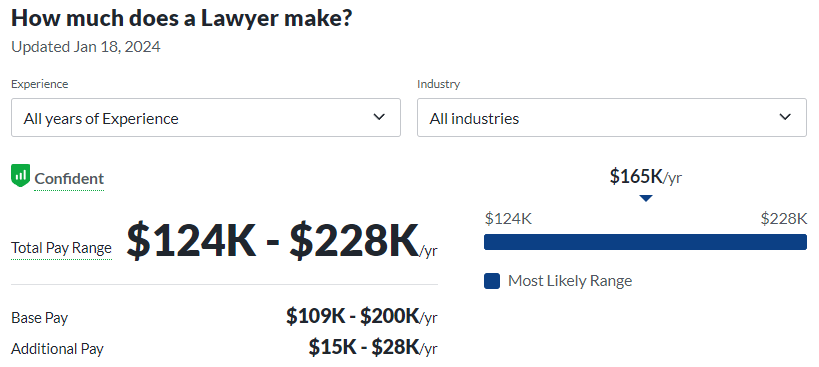
- Policy Research:Engaging in policy research, political theorists contribute valuable insights to the formulation and evaluation of public policies, guided by their analytical skills and theoretical knowledge. This fosters effective governance and addresses societal challenges.
- Interest Groups: Political theorists aligning with interest groups advocate for specific ideologies or policy changes, enhancing the strategic efforts of these groups. They influence public opinion, engage with policymakers, and actively shape the political discourse.
- Advocacy: Advocacy roles allow political theorists to directly promote and defend specific political ideas or values. Whether working for NGOs, think tanks, or grassroots organizations, they contribute to societal change by championing causes aligned with their theoretical understanding of politics and justice.
- Academia and Research: Many political theorists find fulfilling careers in academia and research institutions, contributing to the intellectual development of future leaders, policymakers, and citizens. This path allows for a deep exploration and dissemination of political theories that shape the discourse within and beyond academic circles.
Research Methodologies
Within the diverse landscape of political science, the facet of Research Methodologies stands as a crucial pillar, guiding scholars in their quest for a deeper understanding of political phenomena. This exploration delves into the techniques for data collection and analysis in political science, with a focus on survey design, statistical modeling, and interpreting results.
Techniques for Data Collection/Analysis in Political Science:
Political scientists employ a range of techniques to collect and analyze data, providing insights into the intricacies of political systems and behaviors. These techniques encompass both qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative approaches, such as interviews, case studies, and content analysis, offer in-depth explorations of political phenomena, while quantitative methods utilize statistical tools to analyze numerical data, providing a broader perspective.
Survey Design:
Surveys constitute a cornerstone in political science research, offering a systematic way to gather information from a diverse sample of individuals. Survey design involves crafting well-structured questionnaires that address specific research questions. Political scientists carefully select sample populations, determine survey formats, and utilize various questioning techniques to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Statistical Modeling:
Statistical modeling plays a pivotal role in quantitative political science research. Researchers employ statistical methods to identify patterns, relationships, and trends within data sets. Techniques such as regression analysis, factor analysis, and multivariate analysis allow political scientists to uncover correlations between variables, test hypotheses, and draw meaningful conclusions about political phenomena.
Interpreting Results:
Interpreting results is a nuanced process that requires a deep understanding of statistical findings and their implications for political science theories. Researchers scrutinize statistical significance, effect sizes, and confidence intervals to assess the reliability and validity of their results. Effective interpretation involves placing findings within the broader context of existing political theories and critically evaluating their impact on the understanding of political systems.
In essence, Research Methodologies in political science serve as the toolkit through which scholars navigate the complexities of political phenomena. By adeptly employing techniques for data collection and analysis, refining survey designs, and leveraging statistical modeling, researchers contribute to the continuous advancement of political science knowledge.
Emerging Subfields
As the landscape of the different types of political science evolve, Emerging Subfields have become focal points for scholars seeking to understand the dynamic changes in contemporary societies. This part of the article provides a brief overview of currently expanding areas like digital politics and health policy, which exhibits the intersection of technology, culture, and demographics.
Digital Politics
With the rapid evolution of technology, digital politics has become a vibrant and dynamic subfield, offering insights into the changing nature of political engagement in the digital age. This subfield delves into the impact of digital technologies, social media, and online platforms on political behavior, communication, and governance. Scholars in digital politics analyze the role of social media in shaping public opinion, the influence of online activism on political movements, and the implications of digital communication for political participation.
Health Policy
Health policy has risen to prominence as an essential subfield within political science, reflecting the increasing intersection of politics and public health. This area examines the formulation, implementation, and impact of policies related to healthcare systems, access to medical services, and public health initiatives. Scholars in health policy explore the role of political institutions, ideologies, and advocacy in shaping healthcare outcomes.
New Intersections with Technology, Culture, Demographics:
Political science is increasingly intersecting with various domains, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of contemporary challenges.
- Technology: The integration of technology into political processes, from online voting systems to algorithmic decision-making, is reshaping political dynamics. Researchers explore the ethical implications of technological advancements, cybersecurity in elections, and the digital divide’s impact on political participation.
- Culture: The study of culture in political science has expanded to examine how cultural norms, values, and identities influence political behavior. This includes research on the role of cultural factors in shaping political attitudes, the impact of cultural narratives on policy preferences, and the relationship between political institutions and cultural shifts.
- Demographics: Demographic shifts, such as changing population compositions and migration patterns, are influencing political landscapes. Political scientists are exploring the implications of demographic changes on electoral dynamics, policy preferences, and the representation of diverse voices in political institutions.
In summary, these Emerging Subfields in political science reflect the discipline’s adaptability to contemporary challenges. By delving into digital politics, health policy, and the intersections with technology, culture, and demographics, scholars contribute to a nuanced understanding of the evolving dynamics that shape political systems in the modern era.
Do the Different Types of Political Science Degrees Lead Anywhere?
As we conclude our exploration of Political Science, we’ve uncovered the inner workings of politics and power. From studying various political systems to delving into new areas like digital politics, there’s much to explore. Consider Political Science as a tool that equips you to understand how governments operate, providing the skills to make a real impact. Whether you’re interested in diplomacy, policy decisions, or the connection between politics and technology, the field offers promising avenues.
If you’re curious about understanding the world, intrigued by decision-making processes, and seeking a meaningful career, Political Science could be your pathway. It’s not just a subject; it’s a guide to comprehending and navigating the practical landscapes of political power.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Types of Political Science Degrees
Do any of the different types of Political Science degrees lead to a career outside of government or politics?
While many associate Political Science with direct involvement in government or electoral politics, a degree in this discipline provides a versatile foundation for careers in various sectors. The analytical, research, and communication skills acquired translate well into fields like:
- Nonprofit and Advocacy: Contribute to social change by working with nonprofits focused on issues like education, environmental protection, or human rights.
- Business: Understand the regulatory environment and navigate international markets, roles in compliance, risk analysis, and government relations are in reach.
- Law: A Political Science background provides a strong basis for pursuing a legal career, with applications in areas like policy, civil rights law, and international law.
- Journalism and Media: Report on political events, provide analysis and commentary, or work in public relations and strategic communications.
What’s the difference between Comparative Politics and International Relations?
While both Comparative Politics and International Relations explore global politics, the key difference lies in their focus:
- Comparative Politics focuses on the internal workings of political systems within countries. It analyzes governmental structures, political processes, and how institutions shape societal outcomes.
- International Relations prioritizes the relationships between states, examining diplomacy, foreign policy, international organizations, and the dynamics of conflict and cooperation on a global scale.
Besides the careers mentioned, what are some other unique job possibilities with a Public Administration background?
Public Administration offers diverse career paths beyond traditional government roles. Here are a few unique options:
- Nonprofit Management: Lead non-governmental organizations providing critical social services. Apply your public administration knowledge to strategic planning, fundraising, and program management.
- Budget Analyst: Analyze budget proposals and expenditures for both public and private sector organizations to ensure efficiency and resource allocation.
- City/County Manager: Serve as the administrative head of a local government, overseeing operations, policy implementation, and community development.
- Healthcare Administration: Manage the administrative and operational aspects of healthcare facilities, ensuring quality care and financial stability.
How can someone interested in the philosophical side of Political Theory get involved beyond the classroom?
Theoretical discussions extend far beyond academic settings. Here’s how to engage with Political Theory in the real world:
- Political Think Tanks: Join research teams in think tanks focused on specific ideologies or policy areas. This offers opportunities to contribute to policy analysis and thought leadership.
- Debate Clubs and Forums: Participate in organized debates and discussions exploring contemporary political issues and philosophical underpinnings.
- Blogging and Online Communities: Share your analysis of political ideologies through dedicated blogs or contribute to online political philosophy forums.
- Political Campaigns and Organizations: Volunteer with political campaigns or organizations aligned with your philosophical perspectives and help translate theory into action.
What are some cutting-edge research topics in Emerging Subfields of the different types of Political Science?
Emerging Subfields are dynamic areas offering exciting frontiers for research. Here’s a look at a few hot topics:
- Digital Politics
- Impact of misinformation and disinformation campaigns on elections
- Online political polarization and its effects on democratic discourse
- The development of ethical guidelines for artificial intelligence in politics
- Health Policy
- Comparative analysis of pandemic responses across countries
- Politics of global vaccine distribution and access
- The role of interest groups in shaping health insurance policies

… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 10832 additional Info on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 33834 additional Info to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 83678 more Information on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 87316 more Information to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 75709 more Information on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 57098 more Information on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 48722 additional Info on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: shanehummus.com/college-degrees/types-of-political-science/ […]