Human Resources Management Overview
Human resources management (HRM) has become a critical function in today’s business world. As companies aim to gain a competitive advantage, they realize their people set them apart. HRM oversees the recruiting, development, and retention of talent. This article explores what a human resource management degree entails and why it deserves consideration.
What is Human Resources Management?

HRM plays a key role in maximizing employee performance to meet an organization’s objectives. HR professionals manage compensation and benefits, training, recruitment, employee relations, and more. They ensure compliance with employment laws and strive to create positive work cultures.
HRM plays a key role in maximizing employee performance to meet an organization’s objectives. HR professionals manage a wide range of functions, including:
- Compensation and benefits
- Training
- Recruitment
- Employee relations
- Performance management
- Onboarding
- Policy development
- Workplace safety
- Company culture
Why is HRM Important?
A company’s most valuable asset is its people. Even in our technology-driven world, human insight, creativity, and talent drive innovation and profitability. Forward-thinking organizations recognize that strategic human resources management attracts top talent, motivates employees, increases retention, and boosts productivity. Simply put, the quality of the workforce determines success.
However, many businesses still underutilize the potential of human resources. Old-school companies view employees primarily as expenses rather than strategic assets. They neglect culture, professional development, work-life balance, fair compensation, recognition, and collaboration. This outdated perspective hampers performance, innovation, and retention.
The quality of a company’s workforce determines its success. A skilled HR strategy attracts top talent, motivates employees, increases retention, and boosts productivity. Companies with excellent HR practices outperform the competition.

The Evolving Role of Human Resources Management
Thankfully, mentalities are shifting. Savvy companies now align human resource strategy with key business goals. They leverage HR functions to gain a competitive edge. Fields like training, compensation, recruitment, communications, and technology enhance the employee lifecycle within an organization. Managers collaborate with skilled HR professionals to boost satisfaction, engagement, productivity, and talent acquisition.
This evolution shows why human resources management has become a critical function in today’s business world. HR oversees the most precious company resource—human potential. When done effectively, human resources management plays a vital role in maximizing employee performance to meet an organization’s objectives.
Course Curriculum: Core Concepts and Customization
The well-rounded curriculum covers core HR competencies while allowing concentration. Students take introductory courses, then choose concentration areas, like:
- Recruiting and staffing
- Compensation and benefits
- Employee relations
- Training and development
- HR technology
Introductory courses build foundational knowledge in areas like:
- HR management: Learn to align HR strategy with business objectives.
- Labor relations: study laws and collective bargaining agreements governing management-union relations.
- Staffing: Explore recruitment, selection methods, and retention techniques.
- Total rewards: examine compensation, benefits, work-life balance, recognition, and career development programs.
Students then customize the remaining credits based on their career goals. For example, those interested in training can take courses on instructional design, eLearning technology, measuring learning impact, and coaching skills.
Every concentration integrates practical learning. Through case studies, students apply concepts to real workplace scenarios. This prepares graduates to handle on-the-job HR issues.
Looking to get a human resources management degree from WGU in 6 months? Watch my video about it:

Interdisciplinary Approach: Psychology, Business, and Law
To manage people effectively, HR professionals draw knowledge from various disciplines. HRM programs incorporate psychological, business, legal, and technological perspectives.
For example, a “Training, Learning, and Development” course blends business strategy with the science of learning. Students assess organizational needs, then craft training plans, applying psychology-based instructional methods.
Also, a “Human Relations and Organizational Behavior” course leverages psychology concepts. It develops skills for boosting engagement, managing change, resolving conflict, and promoting diversity and inclusion.
By synthesizing insights from various fields, students gain an expansive understanding of the factors impacting individual, team, and organizational performance. This builds a solid foundation for addressing the complex issues HR professionals face.
Career Pathways for Human Resources Management Graduates
A degree in human resources management opens doors to diverse career opportunities with strong earning potential. There is a high demand for HR professionals across all industries. Graduates build expertise to advance into roles such as:
- Recruiter: Attract top talent by sourcing, interviewing, assessing candidates, and managing hiring processes for an organization.
- Compensation and Benefits Analyst: Monitor pay fairness, design competitive salary and bonus structures, manage benefit programs, and conduct cost analysis.
- HR Generalist: Serve as a strategic business partner to managers on a variety of HR functions like staffing, policy, training, engagement, and labor relations.
- Talent Development Manager: Conduct needs assessments, design training curriculum, and evaluate program effectiveness to enhance employee skills and leadership capabilities.
- Labor Relations Specialist: Interpret collective bargaining agreements and mediate disputes between management and labor unions.
The settings HR professionals work in are as diverse as the field itself. While every type of organization requires human resource functions, students can choose to specialize:
- Corporations
- Healthcare systems
- Government agencies
- Non-profit organizations
- Educational institutions
- Hospitality and retail companies
- Technology and engineering firms
Human resources management graduates are often equipped with knowledge and skills that translate across sectors. For those seeking leadership roles, the pathway can progress from HR Officer to Manager, then Director. The potential for high impact and career advancement makes human resources an appealing, versatile field to enter.
HR Career Demand
A human resources management degree opens doors to diverse HR roles with high earning potential. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 5% job growth for HR managers and specialists from 2022-2032.
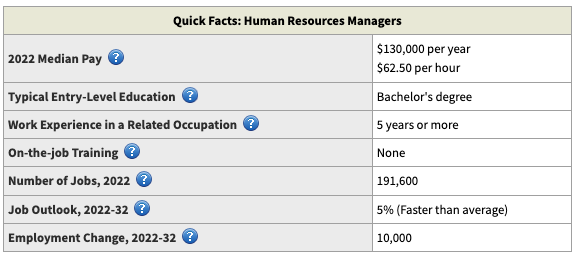
While every organization needs HR functions, students can target their preferred industries and settings. Example pathways include:
- Recruiter for a high-tech firm
- Compensation analyst for a healthcare system
- HR generalist at a retail corporation
- Training coordinator for an engineering company
- Labor relations manager for a public utility
We support career advancement through corporate internships, networking events, career coaching, workshops on interviewing and salary negotiation, and access to job openings. A lot of graduates secure HR roles within six months.
Global, Ethical Perspective
With ever-diversifying workplaces, HR leaders must adopt ethical, socially-responsible, globally-minded perspectives. Human resource degrees embed these values in all courses and activities.
Students complete projects benefiting non-profits and disadvantaged groups. Assignments emphasize sustainable business practices. Courses explore workplace inclusion, unconscious bias, and managing cross-cultural teams.
Together, this develops principled, conscientious professionals prepared to enhance employee wellbeing and organizational success.

Should You Study Human Resources Management?
This field suits those who are passionate about helping employees thrive. HR draws on individuals who:
- Relish managing people-focused initiatives
- Possess integrity, objectivity, and diplomacy
- Can balance employee advocacy with business strategy?
- Want to improve workplace cultures?
The demand for skilled HR professionals will continue to grow. This career promises meaningful work with lucrative, resilient job prospects across sectors.
An innovative human resources management degree will stand out for its student-driven design, real-world application, robust career support, and development of globally-minded managers.
If you aspire to impact organizations by maximizing human potential, this is the perfect path. Watch my video about whether a human resource degree is worth it:
Frequently Asked Questions About a Human Resources Management Degree
What degree is best for HR?
A bachelor’s degree in human resources, business administration, or organizational management provides the best foundation for a career in human resources management. Some schools also offer specialized BS or BA degrees, specifically in HRM.
Is HRM a BS or BA?
HRM degrees can be either a Bachelor of Science (BS) or a Bachelor of Arts (BA), depending on the school and program curriculum. The core content is similar, but a BS may require more math/stats while a BA emphasizes communication skills.
What is BSBA major in HRDM?
A Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (BSBA) with a major in Human Resource Development Management (HRDM) combines the business administration curriculum with specialized courses in HR principles, labor relations, compensation, training, recruitment, and retention.
Does HRM have math?
Most HRM programs require some mathematical background for courses in HR statistics, analytics, and compensation modeling, but not as much math as degrees like engineering or accounting. There is more focus on communication, psychology, ethics, and law.
What does an HR manager need to know?
HR managers should understand employment law, organizational psychology, compensation, benefits, training, recruitment, business strategy, and statistics. Strong communication, ethics, critical thinking, and people management skills are also vital.
