Engineering Degrees: Blueprint to a World of Possibilities
Engineering degrees open up a world of exciting career possibilities in diverse fields that shape the future of technology and society. This article explores key topics related to pursuing an engineering education, including the major branches of engineering, required skills and courses, potential careers and earning potential, the hardest and easiest majors, and the bright outlook for the field.
Whether you dream of designing spacecraft, developing clean energy solutions, or launching a tech startup, an engineering degree provides a flexible foundation to make those goals a reality. This article will help you navigate through the top engineering degrees to make the right choice.
What is Engineering?

Engineering is one of the major fields in the STEM strand. It actively applies scientific, mathematical, and design principles to find solutions for real-world problems and needs. Engineers conceive, analyze, design, and implement systems, structures, processes, components, and materials across nearly every industry.
Engineers tackle complex challenges that impact quality of life, safety, and sustainability. They actively integrate science, technology, and human factors into innovative solutions.
Active engineering fields include:
- Civil engineers design and construct infrastructure like buildings, roads, bridges, tunnels, dams, and water systems. They manage project planning, budgeting, permitting, and construction.
- Mechanical engineers actively analyze, design, simulate, and test mechanical devices and systems ranging from medical equipment to vehicles to industrial automation.
- Electrical engineers actively design, develop, and oversee the manufacturing of electrical equipment, including power systems, telecommunications networks, navigation systems, and electronic devices.
- Chemical engineers actively apply chemical, biological, and physical principles to manage processes that convert raw materials like oil and gas into everyday products like plastics, drugs, and synthetic fibers.
- Computer engineers actively design software, hardware, networking systems, databases, and other computing components that empower modern technology.
- Industrial engineers actively focus on optimizing complex systems and processes by reducing costs, improving quality and productivity, ensuring safety, and integrating sustainability. Their work includes designing manufacturing systems, supply chains, and business operations.
The major branches of engineering solve diverse challenges across industries through innovation, design, and systemic thinking. Engineers actively apply math, science, and technology to build a better world.
Here’s a video about the Best Engineering Degree Tier List:
6 Major Types of Engineering
Civil Engineering
Civil engineers conceive, design, build, manage, and maintain infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, tunnels, buildings, airports, dams, and water and sanitation systems. Their work combines engineering science with project management skills. Civil engineering careers include:
- Construction managers oversee building projects from development to completion.
- Structural engineers design and assess structures like bridges, towers, and stadiums to withstand stresses.
- Transportation engineers plan and engineer systems for road, rail, air, and marine transportation.
- Environmental engineers develop solutions for water quality, recycling, waste disposal, and pollution control.
- Geotechnical engineers analyze geology and soils for siting and designing foundations and underground construction.
Chemical Engineering
Chemical engineers apply physics, chemistry, biology, and engineering principles to oversee processes that convert raw materials like oil, natural gas, water, metals, and food into everyday necessities and products like fuels, plastics, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, detergents, synthetic fibers, microchips, and more. Careers include:
- Process engineers manage and optimize chemical manufacturing processes and production.
- Research engineers develop new chemical processes and design pilot plants to scale up production.
- Plant engineers oversee the operations, efficiency, maintenance, and safety of chemical plants.
- Biochemical engineers design processes using living organisms like bacteria and enzymes.
- Polymer engineers develop plastics and polymeric materials like nylon, Teflon, and epoxy.
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering, considered the broadest engineering discipline, applies physics and materials science principles to analyze, design, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. They work on a wide range of products, from medical devices to spacecraft. Sample careers include:
- Automotive engineers design and test vehicles and components like engines, electronics, and safety systems.
- Aerospace engineers design aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and missiles.
- Biomedical engineers integrate engineering with biology and medicine to develop devices like artificial organs, prostheses, instrumentation, and medical software.
- Manufacturing engineers manage production processes to manufacture products efficiently, cost-effectively, and safely.
- HVAC engineers design heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for buildings and industry.
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineers design, develop, and supervise the manufacture of electrical equipment such as electric motors, communications systems, navigation systems, electronics, and power generation equipment. Careers encompass:
- Electronics engineers design and develop computer systems, telecommunications equipment, and electronic devices.
- Control systems engineers develop control systems for applications ranging from flight control to industrial automation.
- Signal processing engineers focus on analyzing and manipulating signals digitally or through analog circuits.
- Power engineers work on the generation, transmission, and utilization of electric power and energy.
- Microelectronics engineers design, develop, and supervise the fabrication of microelectronic components for computing, communications, aerospace, and other applications.
Computer Engineering/Computer Science
Computer engineers design computer systems and components, including microprocessors, circuit boards, routers, and databases. Careers involve:
- Software engineering: design, develop, test, and maintain software applications and operating systems.
- Computer systems engineering: designing computing systems combining hardware and software components. Focus areas include robotics, cybersecurity, networking, databases, and distributed computing.
- VLSI/Chip Design: Design and develop integrated circuits and CPUs for mobile devices and other electronics.
- Embedded systems: develop microcontrollers and real-time operating systems to interact with physical components in a wide range of applications, from cars to satellites to robots.
Industrial Engineering
Industrial engineers design and optimize complex systems by developing integrated solutions that improve productivity, quality, and efficiency. Their work focuses on reducing costs while ensuring safety and sustainability. Careers in industrial engineering include:
- Manufacturing engineers analyze production processes and design solutions to manufacture products in the most efficient, cost-effective, and safe manner.
- Quality engineers develop test methods and inspection procedures to minimize defects and avoid failures in manufacturing and business processes.
- Ergonomics engineers design tools, workstations, and processes that reduce strain on workers and enhance workplace safety.
- Logistics engineers manage and optimize supply chains, inventory, warehousing, transportation, and distribution networks.
- Operations research analysts use advanced analytical methods like simulation, modeling, and optimization to provide data-driven support for decision making and strategy.
How Much Can You Earn with Engineering Degrees?
Engineering offers excellent earning potential across many specialties. According to Glassdoor salary data, the highest-paying major engineering degrees include:
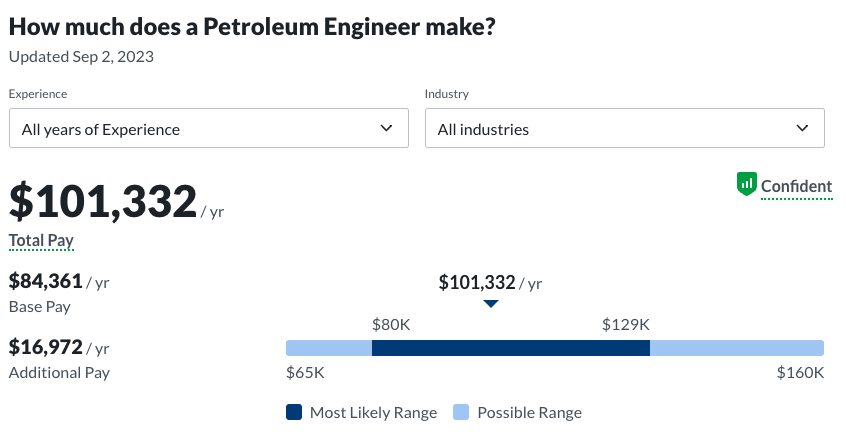
- Petroleum engineering: $101,332 median base salary
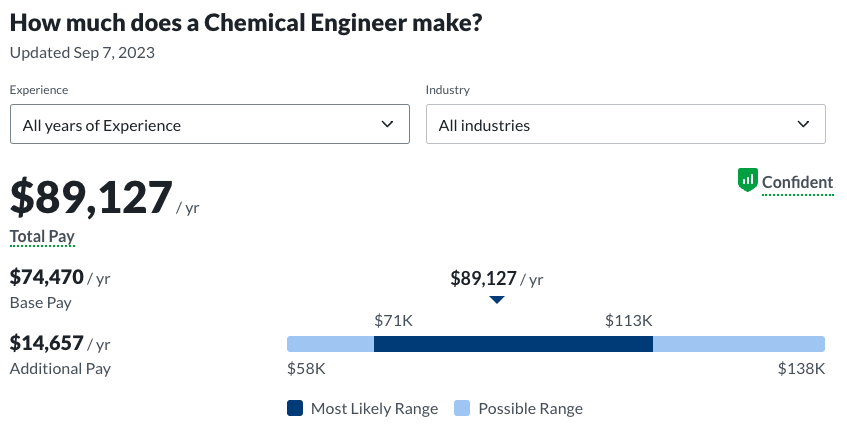
- Chemical engineering: $89,127 median base salary
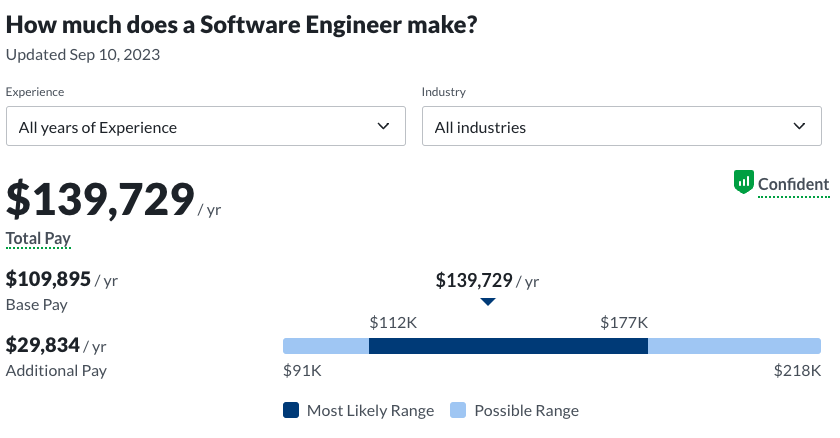
- Software engineering: $139,729 median base salary
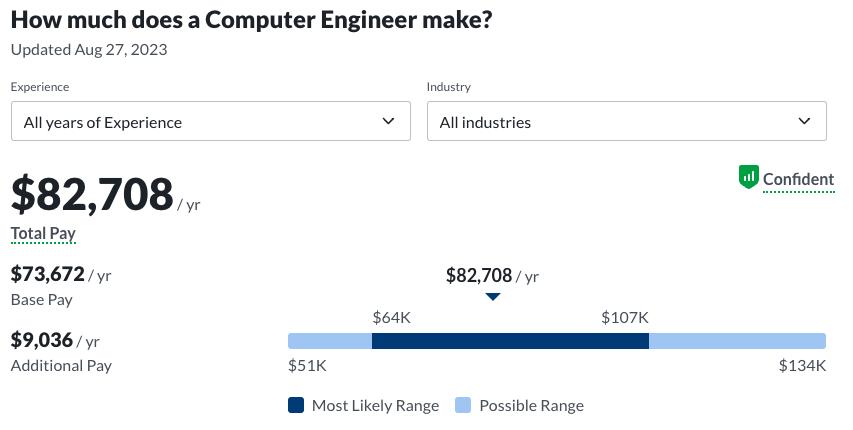
- Computer engineering: $82,708 median base salary
- Aerospace engineering: $132,113 median base salary
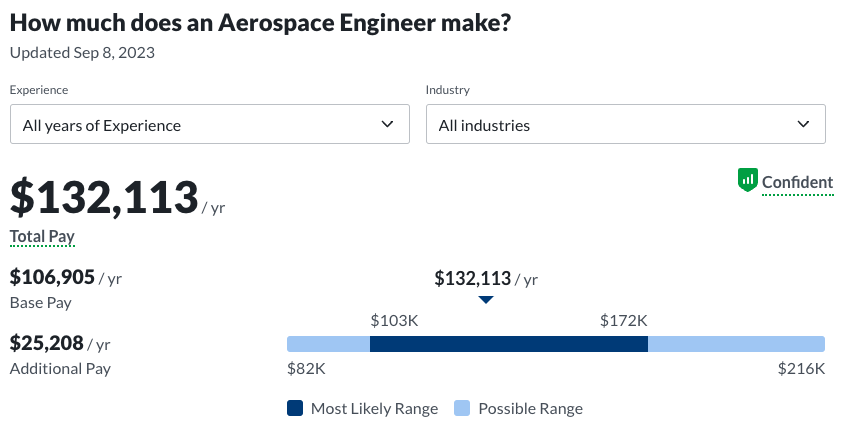
Beyond majors, salaries vary based on industry, location, role, experience, and company size. Engineers with over 20 years of experience can earn $200,000 or more.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for engineers in 2022 was $83,7000, much higher than the median annual wage for all occupations of $46,310. The top 10% of engineers earned over $144,420. Engineering provides strong job prospects and financial stability.
Top 5 Engineering Degrees with High Demand
Certain engineering disciplines are projected to experience faster job growth and have higher demand in the coming years, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The top 5 engineering degrees with the highest demand include:
Software Engineering
Software engineering is expected to grow 25% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations. As software continues to penetrate more products and services across industries, demand for software engineers will remain high.

Computer Engineering
Employment for computer hardware engineers is projected to grow by 5 percent from 2022 to 2032. As computers and electronics are integrated into more everyday devices, systems, and infrastructure, computer engineers will be needed to design the hardware and integrate it with software.

Civil Engineering
Civil engineering employment is projected to grow 5 percent from 2022 to 2032. As population growth drives the need for new infrastructure projects and existing infrastructure ages, civil engineers will be needed to plan, design, and manage construction and maintenance.

Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering jobs are projected to grow 5 percent from 2022 to 2032. As renewable energy expands, telecommunications networks are upgraded, and control systems are implemented in more settings, from vehicles to appliances, the services of electrical engineers will be in demand.

Mechanical Engineering
Jobs for mechanical engineers are expected to increase by 1 percent from 2022 to 2032. Mechanical engineers work on diverse machines and products, from robots and automation equipment to medical devices and new 3D printing technologies. Emerging fields like robotics, renewable energy, and biotechnology will drive demand.

These engineering disciplines offer versatile skills applicable across many growing industries, from software to construction to medical technology. Students interested in job stability and career options may want to consider these high-demand majors.
Want to learn about the WORST engineering degrees? Watch this video!
The Hardest Majors in Engineering
Some of the most challenging engineering majors include:
Aerospace Engineering
- Requires mastery of mechanics, thermodynamics, aerodynamics, astrodynamics, propulsion, controls, avionics, and advanced materials.
- Also involves complex math like multivariable calculus and differential equations.
- Students design planes, rockets, satellites, and space systems. Highly complex topics.
Chemical Engineering
- Coursework covers chemistry, physics, biology, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, heat and mass transfer, plant design, and control theory.
- Students must master abstract concepts and mathematical modeling for chemical processes.
- Careers require keeping up with cutting-edge technologies and research.
Nuclear Engineering
- Involves extensive study of theoretical and applied nuclear physics, including radiation interactions, reactor theory, and nuclear system design.
- Requires knowledge of thermodynamics, fluid flow, heat transfer, and other complex engineering topics.
- Graduates must adhere to strict safety standards for radioactive materials and facilities.
The heavy course loads, abstract concepts, and evolving technologies make these majors intellectually rigorous. Students should be prepared for big workloads.
Easiest Majors in Engineering
While all engineering curricula require strong math and analytical abilities, some majors are considered less intensive in their coursework. Relatively less challenging programs include:
Industrial Engineering
- Focuses more on systems optimization, quality control, and logistics compared to hardcore physics and calculus.
- Touches on areas like production, supply chain, ergonomics, business management, and cost analysis.
- Allows flexibility in electives related to the student’s interests.
Information Systems Engineering
- Emphasizes software engineering and systems integration over intensive math and physics.
- Includes courses in programming, databases, networking, security, project management, and business principles.
- Relatively new and growing field with good career prospects.
Environmental Engineering
- Involves the design and application of solutions for environmental problems vs. advanced theoretical mechanics or physics.
- Allows students to take interesting policy, ecology, and earth sciences electives.
- Opportunity to make a positive impact on sustainability challenges.
The lighter math and physics demands, along with flexibility in electives, make these programs somewhat less rigorous and stressful compared to hardcore engineering disciplines.
Skills You Need for Engineering Degrees
While each engineering specialty requires its own technical expertise, the core skills needed for any engineering program include:
- Math: through differential equations, linear algebra, and statistics
- Science: physics, chemistry, and biology
- Computing: programming, data analysis, modeling
- Design skills: drafting, CAD, prototyping
- Communication: written reports, presentations
- Critical thinking
- Teamwork: Collaborate on projects
- Time management: handle challenging course loads
- Perseverance: Persist through complex assignments
- Creativity: Design innovative solutions
Engineers must be able to apply mathematical and scientific concepts to real-world problems. Analytical ability, communication skills, work ethic, and creativity provide the foundation for success.
Frequently Asked Questions About Engineering Degrees
Which engineering degrees are the easiest?
Generally, industrial engineering, information systems engineering, and environmental engineering are considered less challenging than intensely theoretical disciplines like aerospace and nuclear engineering. However, all engineering curricula require strong analytical and quantitative abilities.
Which engineering field has the highest salary?
Petroleum engineering offers the highest median salary at over $123,230, followed by chemical, software, computer, and aerospace engineering. Experienced engineers can make over $200,000. Salaries vary by role, industry, location, and experience.
Is mechanical engineering hard?
Mechanical engineering includes challenging coursework like statics, dynamics, mechanics of materials, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and mechatronics. Students must apply physics and math to mechanical systems. It’s not the most rigorous discipline, but it still requires strong analytical skills.
Is civil engineering a good career?
Yes, civil engineering offers excellent career prospects. Civil engineers plan, design, and construct infrastructure like roads, bridges, tunnels, dams, and buildings. It’s projected to be one of the fastest-growing engineering fields over the next decade, with good salaries.
Should I get an engineering degree?
If you enjoy math, science, and hands-on problem solving, engineering provides great career opportunities. Graduates work in diverse industries to solve today’s complex challenges. Consider your interests and research different engineering majors to choose the best program.
