STEM Majors: The Game Changers of the 21st Century
Welcome to the world of STEM—the nexus of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics! Here, we unlock the doors to innovation, critical thinking, and the future. STEM is not just a discipline, but a passport to navigating the complexities of the 21st century. Here is where STEM majors come in.
With STEM education, the ordinary becomes extraordinary, and the impossible, possible. Whether it’s the awe-inspiring breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, the intricacies of quantum physics, or the architectural marvels that paint our cityscapes, STEM stands at the heart of it all. Dive in and ignite your curiosity, because with STEM, the world is yours to explore.
What Is a STEM Degree?

A STEM degree focuses on academic qualifications in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It typically involves rigorous study and specialization in one of these disciplines, preparing students for careers that require technical expertise, problem-solving skills, and analytical thinking. STEM degrees cover a wide range of subjects, from physics, biology, and chemistry to computer science, engineering, and mathematics, and they are highly valued in various industries due to the growing demand for professionals with strong STEM backgrounds.
Why is STEM Education So Important?
STEM education is vital because it equips students with the knowledge and skills required to thrive in the modern world. It fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation, which are essential for addressing complex global challenges. STEM fields drive technological advancements, economic growth, and societal progress, making STEM education vital for preparing the workforce of the future and ensuring a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving world.
In the long run, college students who have pursued any of these degree programs have nothing to worry about in terms of career opportunities. The concepts of mathematics, hard sciences, and technology will always have a spot in how our world operates in the next decade and hundreds of centuries to come!
Skills Developed in STEM Majors
hat is STEM?
The STEM field is an interdisciplinary approach that integrates the four domains – Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics – into a unified learning model.
Science
Science is the scaffold on which our understanding of the natural and physical worlds is built. It fuels our curiosity and drives us to ask questions like “Why is the sky blue?” or “What causes a rainbow?” For instance, the path-breaking discovery of DNA’s double helix structure by scientists Watson and Crick has unlocked numerous possibilities in genetics and bio-engineering.
There exist a multitude of bachelor’s degrees that delve into various facets of science, each providing a unique lens through which to comprehend the world around us. Here are a few science majors:
- Degree in Biology
- Degree in Chemistry
- Degree in Physics
- Degree in Environmental Science
- Degree in Geology
The science domain is mostly focused on physical sciences, biological sciences, environmental sciences, natural sciences, and applied sciences.
Technology
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge to create tools that solve real-world problems and enhance our quality of life. From the silicon chips that power our computers to the satellites that connect us globally, technology is an integral part of our everyday lives. Consider the profound impact of inventions like the Internet or smartphone technology, which have revolutionized communication and information access.
Like science, the field of technology also offers an array of academic degrees that prepare students for various roles in the tech world. Here are a few technology majors:
- Degree in Information Technology
- Degree in Web Development
- Degree in Computer Science
- Degree in Cybersecurity
- Degree in Data Analytics
- Degree in Health Information Management
- Degree in Telecommunication
The technology domain is primarily focused on information technology, computer science, software engineering, and other related disciplines. With a degree in one of these fields, individuals can contribute to the vast digital landscape.
Engineering
Engineering is the art of applying scientific and mathematical principles, experience, judgment, and common sense to make things that benefit people. It’s the driving force that takes a concept and turns it into reality, bridging the gap between science and practical application. Engineers design, construct, and maintain everything from skyscrapers to bridges, and from airplanes to smartphones.
The field of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. Here are a few engineering majors:
- Degree in Mechanical Engineering
- Degree in Civil Engineering
- Degree in Electrical Engineering
- Degree in Chemical Engineering
- Degree in Industrial Engineering
- Degree in Architecture or Architectural Engineering
The engineering domain is vast, covering disciplines such as civil engineering, electrical and electronics engineering, mechanical engineering, and chemical engineering, among many others.

Mathematics
Mathematics is the abstract science of number, quantity, and space, either as abstract concepts or as applied to other disciplines such as physics and engineering. It’s the bedrock upon which the other elements of STEM are built, providing the fundamental theories and numeric tools necessary for understanding our world in a quantifiable way. Consider the critical role of mathematical models in predicting weather patterns or the application of statistical probability in risk management and finance.
There are many academic degrees within the field of mathematics, each with its own specific focus. Here are a few mathematics majors:
- Degree in Applied Mathematics
- Degree in Statistics
- Degree in Actuarial Science
- Degree in Operations Research
- Degree in Mathematical Biology
- Degree in Cryptography
The mathematics domain includes areas such as algebra, calculus, statistics, and geometry, among others. By studying mathematics, you not only acquire quantitative reasoning skills, but you also learn to approach problems logically and solve them methodically, skills that are highly transferable and sought after in numerous fields.
Each strand of STEM, while distinct, is interconnected, fostering a holistic approach to problem-solving and innovation. These strands allow college students or STEM students to gain STEM literacy and develop a deeper understanding of these strand’s concepts.

What are STEM Majors?
STEM majors are academic disciplines that fall under the broad categories of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. Here is a list of 20 notable STEM majors:
- Biomedical Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Computer Science
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Information Technology
- Data Science
- Bioinformatics
- Physics
- Chemistry
- Mathematics
- Statistics
- Geological Sciences
- Biochemistry
- Astrophysics
- Marine Biology
Each of these STEM majors offers comprehensive knowledge and practical skills in their respective fields. They pave the way to a plethora of career opportunities in industries at the forefront of innovation and development. If you’re looking for a school to enroll in, a good option would be the Smithsonian Science Education Center.
Most Popular STEM Majors
While there are numerous STEM programs or degrees for STEM graduates, let’s delve into five of the top programs, analyzing their descriptions along with their potential benefits and drawbacks.
Management Information Systems
This degree focuses on the utilization of technology and information systems to support business operations and decision-making processes. Students explore topics such as database management, business intelligence, system analysis, and project management.
Pros:
- High demand for management information systems professionals in various industries.
- Opportunities for career growth and advancement
- Integration of business and technology skills for effective organizational management
Cons:
- Requires a strong understanding of both business and technology concepts.
- Constant need to stay updated with emerging technologies and industry trends.
- Potential challenges in managing complex information systems.
Electrical Engineering
This field revolves around the study, design, and application of electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It covers a wide range of areas, including power systems, electronics, telecommunications, and control systems.
Pros:
- Diverse career opportunities exist in industries such as energy, telecommunications, and electronics.
- Highly transferable skills applicable across different sectors.
- Ability to contribute to technological advancements and innovation.
Cons:
- Requires a solid understanding of advanced mathematics and physics.
- The complexity of electrical systems and circuits may present challenges.
- Potential for high-stress situations, especially in critical infrastructure projects.
Computer Engineering
Computer Engineering combines the principles of electrical engineering and computer science to design and develop computer systems and hardware components. It encompasses areas such as computer architecture, embedded systems, and digital signal processing.
Pros:
- Integration of hardware and software skills for comprehensive system development.
- High demand for computer engineering professionals in industries like telecommunications and consumer electronics.
- Opportunities for innovation in areas such as robotics and IoT
Cons:
- Requires a strong foundation in both electrical engineering and computer science.
- Challenges in designing complex computer systems and optimizing performance.
- Continuous learning is necessary to keep up with advancements in technology.
Software Engineering
This discipline focuses on the design, development, and maintenance of software systems. It involves applying engineering principles to create reliable, efficient, and scalable software solutions.
Pros:
- High demand for software engineering professionals in various industries.
- Opportunities to work on diverse projects and technologies.
- Ability to contribute to the development of innovative software applications.
Cons:
- Requires a strong understanding of programming languages and software development methodologies.
- Challenges in managing complex software projects and meeting deadlines.
- Continuous learning is necessary to stay updated with evolving programming languages and frameworks.
Computer Science
Computer Science delves into the theoretical and practical aspects of computing. It covers areas such as algorithms, data structures, programming languages, and artificial intelligence.
Pros:
- High demand for computer science professionals across diverse sectors.
- Opportunities for innovation and research in emerging technologies.
- Ability to solve complex problems using computational thinking.
Cons:
- Requires continuous learning due to rapidly evolving technology.
- Challenges in mastering complex algorithms and data structures.
- Potential for long work hours, especially during project deadlines.
Best STEM Majors
Determining the “best” STEM majors largely depends on an individual’s interests, career goals, and aptitudes. Here are some majors often recognized for their educational value and career potential:
Electrical Engineering:
Electrical Engineering focuses on the study and application of electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. This field plays a crucial role in the development of cutting-edge technologies in various sectors, such as telecommunications, electronics, and energy.
Pros:
- Robust job market with various industries seeking electrical engineers.
- Excellent salary potential.
- High potential for innovation, especially in burgeoning fields like renewable energy and electric vehicles.
Cons:
- Requires a thorough understanding of complex mathematical and scientific concepts.
- Can require demanding work schedules, especially when project deadlines loom.
- Rapid technological advancements necessitate a commitment to lifelong learning.
Salary for Electrical Engineers:
According to Glassdoor, the salary for Electrical Engineers can vary based on location, industry, experience, and role. The median annual wage in August 2023 will be $96,903. Entry-level positions may start at around $64,000, but with experience and qualifications, it can increase significantly. Senior electrical engineers can earn over $148,000 per year. Additional benefits and bonuses may also be included.
Physician Associate:
Physician Associate is an advanced STEM education and healthcare profession that involves working alongside physicians and other healthcare professionals to provide patient care. They perform tasks such as taking medical histories, conducting physical examinations, and prescribing medications under the supervision of a physician.
Pros:
- Growing demand for physician associates in healthcare settings.
- Competitive salary potential.
- Opportunity to make a positive impact on patient care.
Cons:
- Requires extensive medical knowledge and training.
- May involve long hours and high levels of responsibility.
- Ongoing professional development is necessary to stay current in the field.
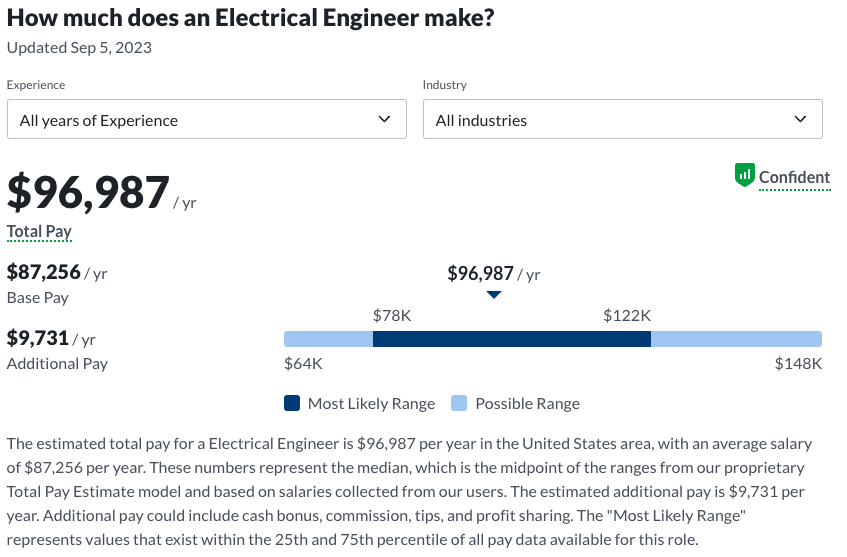
Salary for Physician Associates:
As per Glassdoor, the salary for Physician Associates can fluctuate depending on factors such as geographical location, the healthcare sector, years of experience, and specific roles. As of June 2023, the median annual income was approximately $98,770. Entry-level positions can expect to earn around $60,000, but this can rise significantly with experience and specialist qualifications. Senior Physician Associates can see earnings in excess of $163,000 annually.
Computer Engineering:
Computer Engineering combines the principles of electrical engineering and computer science to design and develop computer hardware and software systems. It encompasses areas such as computer architecture, digital systems, and embedded systems.
Pros:
- Strong demand for computer engineering professionals in various industries.
- Lucrative salary potential.
- Opportunity to work on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.
Cons:
- Requires a solid understanding of both electrical engineering and computer science concepts.
- Can involve long hours and tight deadlines for project completion.
- Constant learning and keeping up with advancements in technology are necessary.
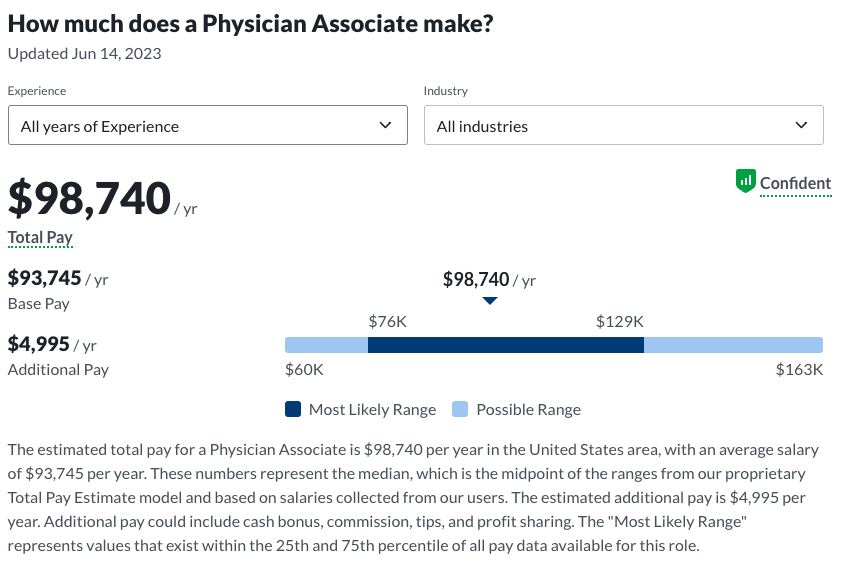
Salary for Computer Engineers:
According to Glassdoor, the salary for Computer Engineers can vary widely based on location, industry, experience, and specific roles. The median annual wage in August 2023 is approximately $83,036. Entry-level positions may start at around $52,000, but this can rise considerably with experience and enhanced qualifications. Senior Computer Engineers can earn over $135,000 per year.
Software Engineering:
Software Engineering involves the design, development, and maintenance of software systems. It focuses on applying engineering principles to create high-quality software solutions that meet user requirements.
Pros:
- Growing demand for software engineers in industries ranging from tech to healthcare.
- Excellent salary potential.
- Opportunity to work on innovative projects and solve complex problems.
Cons:
- Requires strong programming and problem-solving skills.
- Can involve long hours and tight deadlines, especially during the software development lifecycle.
- Continuous learning and staying updated with new technologies are essential.
Salary for Software Engineers:
Based on the data from Glassdoor, the salary for Software Engineers can differ substantially according to geographical location, industry, years of experience, and specific roles. As of August 2023, the median annual wage is approximately $139,713. Beginners in the field may commence their careers with a salary of around $91,000, but this can see a significant upswing with experience and additional qualifications. Senior Software Engineers can anticipate earnings that exceed $218,000 annually.
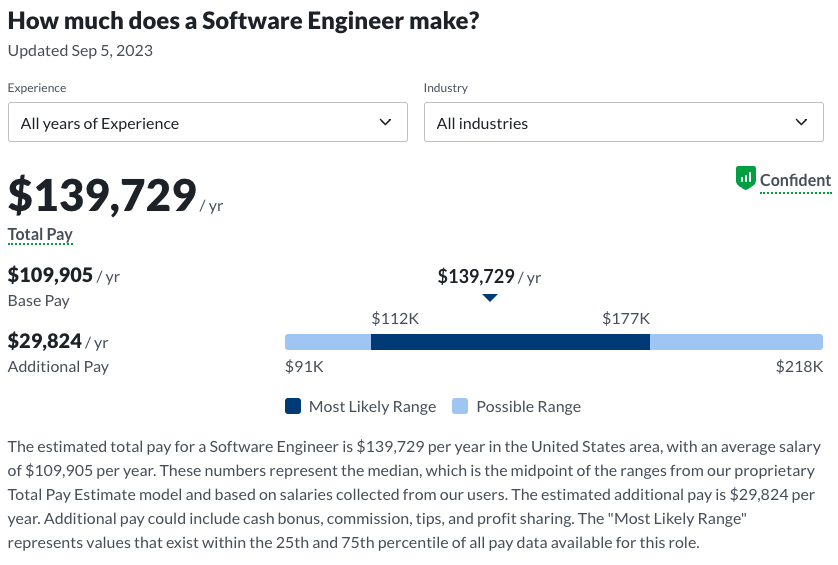
Computer Science:
Computer Science encompasses the study of algorithms, programming languages, data structures, and computer systems. It involves both theoretical foundations and practical applications in various domains.
Pros:
- Wide range of career opportunities in diverse industries.
- Competitive salary potential.
- Opportunities for research and innovation.
Cons:
- Requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Can involve long hours of coding and debugging.
- Constant learning and staying up-to-date with advancements in the field are necessary.
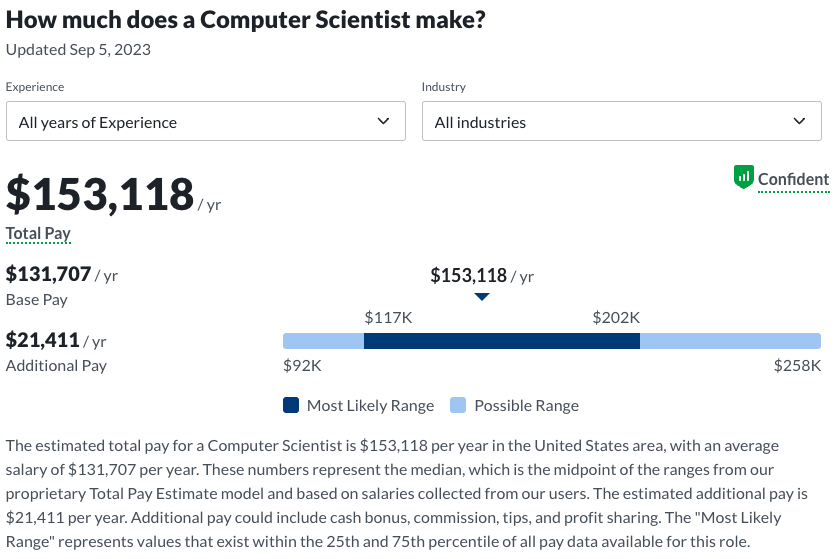
Salary for Computer Scientists:
According to information from Glassdoor, the earnings for those in the field of Computer Science can vary significantly based on factors such as location, industry, experience, and specific roles. The median annual wage in June 2023 was around $95,283. Those just starting their careers in the field might begin with salaries in the vicinity of $55,000, but with additional experience and qualifications, this figure could rise substantially. Veteran Computer Scientists can expect to see earnings surpassing $174,000 per year.
Here are some videos that talk about the highest-paying STEM majors:
Easiest STEM Majors
While the term “easy” is subjective and relative to each student’s strengths and passions, some STEM majors are typically considered less demanding due to their course structure and content. Here are three such majors:
Information Technology (IT)
IT is often seen as one of the easier STEM majors due to its balance between theory and hands-on practice. Unlike Computer Science, which delves deep into complex algorithms and data structures, IT focuses more on practical applications like troubleshooting, network management, and system administration. This focus lends itself to a more accessible and tangible learning experience.
Psychology
While Psychology is indeed a science and thus falls under the STEM umbrella, it is often viewed as less mathematically intensive than other STEM majors. The primary focus lies in understanding human behavior, cognition, and emotion, making it more approachable for students who may struggle with heavy quantitative content. However, it’s important to note that success in Psychology does require strong skills in research and data analysis.
Environmental Sciences
While this major still requires understanding complex systems and conducting research, the coursework is often viewed as more diverse and less math-intensive than in other science fields. The multidisciplinary nature of Environmental Science, which touches on everything from geology to ecology to policy, can make it an engaging and accessible choice for students with broad interests in the natural world.

What are STEM Jobs?
STEM jobs are positions in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. These roles are in high demand and cover a wide range of professions, from research scientists to software developers, and from civil engineers to data analysts.
These critical jobs drive innovation, competitiveness, and economic growth, requiring a robust understanding of STEM disciplines. We’ll dive deeper into the skills required for a STEM job.
The Skills Required for STEM Jobs
While specific skills will depend on the job role, there are a few common skills that are generally required in STEM employment. These include:
- Analytical skills: The ability to analyze data and use it to solve problems is key in all STEM jobs.
- Creativity: Although often overlooked, creativity is essential in STEM to innovate and come up with new solutions or approaches.
- Technical skills: Proficiency in the technical aspects of the job, whether that be a specific programming language, laboratory techniques, or knowledge of engineering principles.
- Teamwork: Many STEM professionals work as part of a team, making the ability to work well with others a crucial skill.
- Lifelong learning: Technology and scientific understanding are constantly evolving. Therefore, STEM professionals must be committed to continual learning and keeping up with the latest developments in their field.
Top 10 High-Paying STEM Jobs
- Petroleum Engineers: These professionals are involved in the extraction and production of oil and gas. They utilize the latest technology to drill and produce oil in the most efficient manner.
- Computer Network Architects/Engineers: They design and build data communication networks, such as local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and Intranets.
- Pharmacists: They dispense medications to patients and offer expertise in the safe use of prescriptions.
- Aerospace Engineers: These professionals design and test aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and missiles.
- Computer Hardware Engineers: They research, design, develop, and test computer systems and components.
- Nuclear Engineers: They research and develop the processes, instruments, and systems used to garner benefits from nuclear energy and radiation.
- Software Developers: They create the applications or systems that run on a computer or another device.
- Physicists: They study the ways in which various forms of matter and energy interact.
- Data Scientists: They analyze and interpret complex digital data to help companies make decisions.
- Medical Scientists: They conduct research aimed at improving overall human health.
STEM Degrees: Opening Up the Future
In summary, STEM careers are diverse and dynamic, spanning a wide range of sectors from computer science and information technology to psychology and environmental sciences. Whether you aspire to engineer the next breakthrough in petroleum extraction, design complex computer networks, develop innovative software, or unravel the mysteries of human behavior, a STEM major can lead to rewarding and high-paying job opportunities.
These roles are critical for driving innovation, competitiveness, and economic growth. Essential skills for STEM careers include analytical capabilities, creativity, technical proficiency, teamwork, and a lifelong commitment to learning. With such a wealth of opportunity at your fingertips, the path to a fulfilling STEM career is wide open.
Frequently Asked Questions About STEM Degrees:
What are considered STEM Degrees?
A STEM degree is any program of study in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This includes a vast range of disciplines, from the more traditional areas like physics, chemistry, and biology to newer fields like information technology, data science, and environmental science. Such degrees focus on technical skills and problem-solving approaches, preparing students for a wide variety of high-demand careers.
Is STEM the best strand?
Whether STEM is the best strand depends on a student’s interests, strengths, and career goals. STEM disciplines offer a wide range of high-paying job opportunities and are in high demand in the modern workforce. However, success in STEM requires strong skills in problem-solving, analytical thinking, and technical proficiency. For those who enjoy these areas, STEM could indeed be the best strand.
Why do people choose STEM majors and strands more?
People often choose the STEM strand due to the diverse and promising career prospects it offers. The demand for professionals in fields such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics is high, often resulting in competitive salaries and job security. Furthermore, the STEM strand enables individuals to contribute to innovation, technological advancement, and problem-solving on a global scale.
What is the hardest major in STEM?
The hardest major in STEM is subjective and depends on a student’s strengths and interests. However, many students find the Bachelor’s Degree in Physics to be the most challenging. This is due to the complex mathematical concepts, abstract theories, and rigorous problem-solving it entails. Nonetheless, despite its difficulty, Physics can also be incredibly rewarding and opens up a wide range of career options.
How do I pick a STEM strand?
Choosing a STEM strand should be a thoughtful process based on personal interests, academic strengths, and long-term career goals. Start by identifying which STEM subjects you find most exciting and engaging. Then, research potential careers related to those subjects to understand the skills required and the job outlook. Speaking with professionals in the field or seeking academic guidance can also be helpful. Ultimately, make a choice that aligns with your passion and aspirations.
